IB Physics HL - 2024 - Questionbank
2.3 - Work, Energy, and Power
Work, Kinetic Energy, Gravitational & Elastic Potential Energy, Power, Conservation of Energy, Efficiency
Question Type
All
Paper
Difficulty
View
Question 1
Which of the following units is not a unit of power?
-
A. W
-
B. J
-
C. N m s
-
D. J s
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 2
A builder uses a block and tackle pulley system to lift a bundle of materials of mass 15 kg to the top of a building of height 6 m in 9 s. What is the power delivered to the bundle? Assume .

-
A. 10 W
-
B. 17 W
-
C. 100 W
-
D. 900 W
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 3
A box is pulled by a child with a horizontal force of 5 . The box moves a horizontal distance of 4 in a time of 2 . The average power delivered by the child to the box is
-
A. 2.5
-
B. 5.0
-
C. 10
-
D. 40
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 4
Which of the following is not appropriate for measuring energy?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 5
A box of mass m is pulled across a horizontal surface with a force as shown in the diagram. The coefficient of dynamic friction between the box and the surface is µ. What is the energy transferred to thermal energy while a box is moved by a distance of ?

-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 6
A block of mass 16 kg is pushed and released along a rough horizontal surface at an initial speed of .

The block travels through a distance of 16 m and is brought to rest. What is the magnitude of the frictional force that brings the block to rest?
-
A. 2 N
-
B. 4 N
-
C. 8 N
-
D. 16 N
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 7
The engine of a racing car provides a forward thrust of . The average of the total resistive forces acting on the car is and the car covers a distance of in .
What is the average output power of the engine?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 8
An electric motor is used to raise a block of mass 18.0 kg vertically to the top of a building at a constant speed of . If the power rating of the motor is 297 W, calculate the efficiency of the motor. Assume
-
A. 9%
-
B. 75%
-
C. 61%
-
D. 91%
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 9
A box is pulled up a slope inclined at 30° to the horizontal by a force of . The angle between the direction of and the plane of the incline is also 30°.
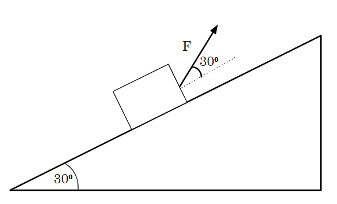
The box is pulled a distance of d up along the slope. What is the work done by F on the box?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 10
[Maximum mark: 9]
-
A ball of mass moving on a frictionless horizontal plane collides elastically with a vertical wall.

The variation of the force acting on the ball during the collision with time is shown on the graph below.

The speed of the ball just before the impact is . Calculate the maximum force exerted on the wall by the ball. [3]
-
The wall is covered with a coating that causes an inelastic collision. The ball hits the wall with the same initial speed and bounces back with a speed of .
-
Explain, by considering the moments just before and after the collision, how the principle of conservation of energy applies to the collision. [2]
-
Calculate the loss of the energy of the ball during the collision. [2]
-
During this collision, the ball undergoes a change in momentum. Discuss whether the the law of conservation of momentum applies in this situation. [2]
-
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video (a)
Video (bi)
Video (bii)
Video (biii)
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 11
A spring that obeys Hooke's Law is stretched a distance and stores energy .
What is the work done by the spring when it returns to the point where is reduced to half of its original value?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 12
A car engine has an input power of P and efficiency of . Which of the following gives the wasted energy from the engine in time of ?
-
A. P t
-
B. P
-
C. Pt - P t
-
D. Pt -
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 13
A boat is traveling along a straight line for a total time of one hour. The boat travels at a constant speed and covers a total distance of 2.4 . The thrust of the boat’s engine is 1.8 .
What is the energy exerted by the boat’s engine in one second?
-
A. 0.67
-
B. 1.2
-
C. 4.3
-
D. 78
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 14
A box of mass starts to move on a level surface under the effect of a varying force . The variation of with the displacement of the object is shown in the graph below.

What is the speed of the box at ?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 15
A varying force acts on a spring. The variation of the extension of the spring with force acting on it is shown in the graph below.

The elastic potential energy stored in the spring is when the extension of the spring is . What is the work done by force on the spring to increase the extension from to ?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 16
[Maximum mark: 12]
An elastic bungee cord of natural length is being tested. A spherical object, originally at rest, is released from a platform. Air resistance and the mass of the cord are insignificant.

-
State the principle of conservation of energy. [2]
-
Describe the energy changes that take place in the spherical object from the time it is released until it comes to rest for the first time. [2]
-
Show that the speed of the object just before the cord starts to extend is approximately . [2]
-
The magnitude of the average force acting on the object by the cord between the point the cord starts to extend and the point where it reaches maximum extension is . The time taken during the fall of the object between these points is .
-
Show that the mass of the object is approximately . [2]
-
On the graph below, sketch how the the elastic potential energy of the spring changes with the vertical displacement as the cord stretches. There is no need to add values to the axes. [2]

-
The extension of the cord at the point in time when the object has zero acceleration is . Determine the spring constant of the cord. [2]
-
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 17
A robot is used to move boxes in a factory. A box is pulled up a slope inclined at 30 to the horizontal by a rope connected to the robot. The tension in the rope is . Friction acts between the box and the ramp.

- Define work done by a force. [2]
-
The box is moving at a constant speed. It covers in .
-
Show that the output power of robot . [2]
-
During the pull, the robot has a potential difference of across the terminals of its battery and a current of derived from the battery. Determine the efficiency of the robot in this situation. [2]
-
The emf of the battery is 32 . Calculate the internal resistance of the battery. [2]
-
-
The rope connecting the robot and the box breaks at a height of from the ground level.
-
The maximum height above the ground level reached by the box is . Show that the work done by friction on the box after the break up to reach the maximum height is . [2]
-
Determine the coefficient of dynamic friction between the box and the incline. [3]
-
The box experiences friction both on the way up the slope and also as it slides back down the slope. On the graph below, sketch the variation of the speed of the box with the time passed from when the rope breaks until the box reaches the ground level. [2]

-
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video (a)
Video (bi)
Video (bii)
Video (biii)
Video (ci)
Video (cii)
Video (ciii)
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 18
A spring of spring constant is compressed by . A box is placed against the spring.

At the point where the box has moved , how much work has been done by the spring on the box?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 19
An object is thrown vertically upwards on the surface of the moon. The maximum height that the object can reach is h. When the object reaches the height of above the surface, what is the ratio
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 20
A motorised toy car starts from rest, with the motor delivering increasing power to the car over time as shown in the graph below.

Assuming no energy losses, which of the following gives the kinetic energy of the car after 8.0 seconds?
-
A. 0.20 J
-
B. 5.0 J
-
C. 160 J
-
D. 320 J
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 21
A motor uses a cable to pull a trolley up an inclined plane at a constant velocity.

Which of the following statements about the energy changes of the trolley during its motion are correct?
-
I. The work done by the engine has greater magnitude than the work done by friction. II. The total of kinetic and potential energy of the trolley increases. III. The gain in gravitational potential energy of the trolley has the same magnitude as the work done by the engine.
-
A. I and II only
-
B. I and III only
-
C. II and III only
-
D. I, II and III
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 22
A ball is released from rest at a height h above the ground. At each bounce At each bounce 75% of its kinetic energy is lost. Which graph represents the variation of the ball's velocity v with time t from the beginning of motion until the moment just before the third bounce? Assume the acceleration of the ball is in in the negative direction and that air resistance is negligible.
| A. | B. | |||
 |  | |||
| C. | D. | |||
 |  |
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 23
A box of mass is pushed with an initial speed of on a rough horizontal floor. A uniform frictional force of acts on the box. What is the distance travelled by the box at the instant when the kinetic energy of the box is halved?
-
A. 10 m
-
B. 5 m
-
C. 2 m
-
D. 1 m
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 24
[Maximum mark: 11]
-
Define power. [2]
-
A mass of 2.0 is pulled by a variable horizontal force on a smooth surface. A thread attached to the mass passes over an ideal pulley and supports another mass of 3.0 .

The variation of with the distance moved by the mass of 2.0 is shown in the graph.

-
Calculate work done, in , on the 2.0 mass by the force when the mass travelled 0.90 . [2]
-
Calculate the final speed of the 2.0 mass. [3]
-
-
On another occasion, the horizontal force is no longer applied and the 2.0 mass is replaced with a motor which pulls the 3.0 mass with a constant speed of 0.50 .

-
On the graph, show the variation of the change in gravitational potential energy of the mass with time . [2]
(no need to add values to the axes)

-
The power supplied to the motor is 20 . Calculate the efficiency of the motor. [2]
-
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video (a)
Video (bi)
Video (bii)
Video (ci)
Video (cii)
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 25
[Maximum mark: 11]
-
The diagram below shows a water slide. As a test, an object is released from point , 6.0 above the ground level. Point at the end of the slide is 2.0 above the ground level. Location is the point of contact of the slide with the ground. The slide approximates a circular shape at this point.

Air resistance and friction on the object are negligible.
-
Draw the free-body diagram of the forces acting on the object as it passes point . [2]

-
At the instant the object passes point , explain why there is acceleration and yet no work is done. [2]
-
-
The object slides from point to point and is launched from point with an angle.
-
Show that the speed of the object at point is approximately [2]
-
At point , the object is launched into the air and lands in a pool of water that is 2.2 below point .

After 1.1 , it reaches the surface of the water. Show that the angle of the launch above the horizontal is approximately 22. [3]
-
Calculate the horizontal distance travelled by the object between losing contact with the slide and reaching the water. [2]
-
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video (ai)
Video (aii)
Video (bi)
Video (bii)
Video (biii)
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 26
A system that consists of two light identical springs connected in series stores a total elastic potential energy when a load is added to the springs. One of the springs is then removed and the same load is added to the remaining spring.

In terms of , what is the total elastic potential energy stored in the single spring situation?
-
A. 2
-
B.
-
C. 0.5
-
D. 0.25
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 27
The graph shows the variation of length of a spring of original length as it is stretched to length by a variable force

The work done against the spring is represented by which of the following?
-
A. The area marked X.
-
B. The area marked Y.
-
C. The area marked Z.
-
D. The sum of the areas marked Y and Z
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 28
A race car starts to race on a straight horizontal race track from rest. The car's engine has a constant power output and the car experiences a resistive force that increases proportionally with its speed.
Which graph represents the variation with distance of the power required by the engine to overcome the resistive force?
| A. | B. | |||
 |  | |||
| C. | D. | |||
 |  |
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 29
A trapeze artist is swinging from position A to position C as shown in the diagram.

The combined mass of the artist and the swing is 70 , the length of the rope of the swing is and the tension in the rope at position B is .
Which expression gives the kinetic energy at position B?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 30
A roller coaster goes around the inside of a loop of radius , shown in the diagram. The combined mass of a car and the passengers is .

When the car is at its highest point, the normal reaction force of the track on the car is equal to half of the weight of the car and passengers.
Which expression gives the kinetic energy at the top of the loop?
-
A. 0
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 31
An object is released from rest from a very high building. Air resistance is not negligible. Which of the following graphs shows the variation of the gravitational potential energy of the object with time?
| A. | B. | |||
 |  | |||
| C. | D. | |||
 |  |
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 32
Two masses of and are connected with a string that passes over a pulley. They are released from rest. Energy is lost in the pulley due to friction.

When the mass has gained a gravitational potential energy of , the mass has a kinetic energy of . How much energy has been lost to friction up to that point in time?
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 33
A metal ball of mass is released from a height of above a massless platform attached to a vertical spring.

The spring constant of the spring is given by . The ball hits the spring and compresses it. When the spring is compressed by a distance , what is the speed of the ball?
(Energy transfer only happens between spring and ball and the kinetic energy of the spring can be ignored)
-
A.
-
B.
-
C.
-
D.
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 34
[Maximum mark: 11]
-
Define potential energy. [1]
-
A body of mass 2.0 is pushed with an initial speed of 1.2 down the slope of a frictionless 30 incline from a height of . As soon as it reaches the bottom of the incline, it begins to move on a rough horizontal table where it comes to rest momentarily after colliding with a spring of spring constant 32 . (Air friction is ignored)

-
The speed of the body is 3.06 when it reaches the bottom of the incline. Calculate . [2]
-
The distance between the bottom of the slope and the body's position is . On the graph, sketch the variation of the square of the speed of the body with distance
(no need to add values to the axes)

-
At the instant that the body stops momentarily, the spring is compressed as 0.43 . The coefficient of friction between the body and the rough surface is 0.40. Determine the distance that the body covered on the horizontal rough surface between the point of leaving the ramp and stopping momentarily. [4]
-
-
The incline is replaced with one of a steeper gradient. The body is pushed at the same speed from the same height. Explain the effect of the increase in gradient on the maximum compression of the spring in comparison to the maximum compression in the original situation. [2]
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video (a)
Video (bi)
Video (bii)
Video (biii)
Video (c)
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 35
A 74 kg boy starts to ride a 6.0 kg bicycle from rest. The graph shows how the acceleration of the bicycle varies with the distance travelled .

What is the total work done by the boy?
-
A. 0.3 kJ
-
B. 3.7 kJ
-
C. 4.0 kJ
-
D. 6.0 kJ
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 36
An object of mass rests on a rough surface. Another object of mass is connected to it with a string.

When the objects are released, the masses accelerate at . The work done by the tension of the string on the mass is . Which of the following is correct for the mass during this period?
| Magnitude of the force of friction /N | Distance travelled | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | 10 | |
| B. | 5 | |
| C. | 10 | |
| D. | 5 |
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Video
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Solutions
Revisit
Ask Newton
Question 37
A mass of is hung on the end of the spring. When the system is in equilibrium, the elastic potential energy stored in the spring is .
A downward force is then applied to the system causing the total elastic potential energy stored to double. This is shown in the diagram below.
 [© Revision Village 2022. Created with https://chemix.org/]
[© Revision Village 2022. Created with https://chemix.org/]
The downward force is then removed, and the system oscillates about the equilibrium position.
What is the magnitude of the downward force and the kinetic energy of the mass as it passes the equilibrium position?
You may assume friction and air resistance are negligible.
| Magnitude of downward force | Kinetic energy of mass as it passes equilibrium | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | ( - 1) | |
| B. | ( - 1) | (3 2 |
| C. | ||
| D. | (3 2 |
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Check with RV Newton
Formula Booklet
Mark Scheme
Revisit
Ask Newton
Thank you Revision Village Members
#1 IB Math Resource
Revision Village is ranked the #1 IB Math Resources by IB Students & Teachers.
34% Grade Increase
Revision Village students scored 34% greater than the IB Global Average in their exams (2021).
80% of IB Students
More and more IB students are using Revision Village to prepare for their IB Math Exams.
More IB Physics HL - 2024 Resources
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the IB Physics HL Questionbank?
The IB Physics HL Questionbank is a comprehensive set of IB Physics exam style questions, categorised into syllabus topic and concept, and sorted by difficulty of question. The bank of exam style questions are accompanied by high quality step-by-step markschemes and video tutorials, taught by experienced IB Physics teachers. The IB Physics HL Question bank is the perfect exam revision resource for IB students looking to practice IB Physics exam style questions in a particular topic or concept in their IB Physics Higher Level course.
Where should I start in the Physics HL Questionbank?
The IB Physics HL Questionbank is designed to help IB students practice Physics HL exam style questions in a specific topic or concept. Therefore, a good place to start is by identifying a concept that you would like to practice and improve in and go to that area of the Physics HL Question bank. For example, if you want to practice Physics HL exam style questions covering Momentum & Impulse, you can go to Physics HL Topic 2 (Mechanics) and go to the Momentum & Impulse area of the question bank. On this page there is a carefully designed set of IB Physics HL exam style questions, progressing in order of difficulty from easiest to hardest. If you’re just getting started with your revision, you could start at the top of the page with the easiest questions, or if you already have some confidence, you could start at the medium difficulty questions and progress down.
How should I use the Physics HL Questionbank?
The Physics HL Questionbank is perfect for revising a particular topic or concept, in-depth. For example, if you wanted to improve your knowledge of Forces, there are over 20 IB Physics HL exam style questions focused specifically on this concept. Alternatively, Revision Village also has an extensive library of Physics HL Practice Exams, where students can simulate the length and difficulty of an IB exam with the Mock Exam sets, as well as Physics HL Key Concepts, where students can learn and revise the underlying theory, if missed or misunderstood in class.
What if I finish the Physics HL Questionbank?
With an extensive and growing library of full length IB Physics HL exam style questions in the Physics HL Question bank, finishing all of the questions would be a fantastic effort, and you will be in a great position for your final exams. If you were able to complete all the questions in the Physics HL Question bank, then a popular option would be to go to the Physics HL Practice Exams section on Revision Village and test yourself with the Mock Exam Papers, to simulate the length and difficulty of an actual IB Physics HL exam.